Decentralized Finance (DeFi) has gained significant popularity and has numerous use cases. Here are some of the popular use cases of DeFi:
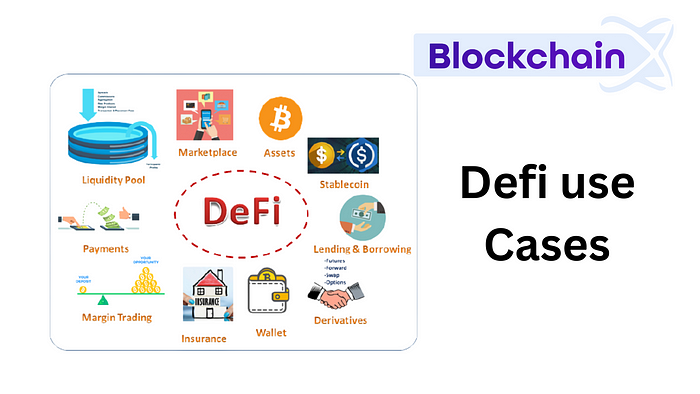
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) use cases offer several benefits over traditional financial systems. Here are some of the key advantages:

- Decentralized Lending and Borrowing: DeFi allows individuals to lend and borrow funds without relying on traditional intermediaries such as banks. Users can lend their cryptocurrencies and earn interest or borrow assets using their crypto holdings as collateral.
- Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs): DeFi has revolutionized the concept of exchanges by introducing decentralized exchanges. These platforms enable users to trade cryptocurrencies directly from their wallets without the need for intermediaries or custodial services.
- Stablecoins and Stablecoin Trading: Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable value by pegging them to a reserve asset, typically a fiat currency. defi use cases has popularized the use of stablecoins, which provide stability and can be used for trading, remittances, and as a store of value within the decentralized ecosystem.
- Yield Farming: Yield farming, also known as liquidity mining, involves users providing liquidity to DeFi protocols in exchange for earning rewards. Users can stake their tokens or provide liquidity to various liquidity pools, enabling them to earn additional tokens or fees.
- Decentralized Insurance: DeFi platforms are exploring the concept of decentralized insurance, where users can purchase coverage against various risks without relying on traditional insurance providers. This enables more accessible and customizable insurance solutions.
- Decentralized Asset Management: DeFi offers decentralized asset management platforms that allow users to manage and invest their funds directly without relying on traditional asset management firms. These platforms often utilize smart contracts to automate investment strategies.
- Prediction Markets: DeFi has facilitated the development of prediction markets, where users can speculate on the outcome of various events, such as elections, sports events, or even cryptocurrency prices. These markets provide a decentralized way for users to make predictions and potentially earn rewards.
- Decentralized Identity: DeFi has also explored decentralized identity solutions, where users can maintain control over their personal information and selectively share it with different entities without relying on centralized authorities.
DeFi (Decentralized Finance) use cases offer several benefits over traditional financial systems. Here are some of the key advantages:
- Financial Inclusion: DeFi opens up financial services to individuals who are unbanked or underbanked. With defi use cases, anyone with an internet connection can access financial tools and services, regardless of their geographical location or socioeconomic status.
- Accessibility: DeFi eliminates the need for intermediaries, such as banks or brokers, making financial services more accessible to a broader range of people. Users can participate in lending, borrowing, trading, and investing directly from their digital wallets without requiring permission or going through complex processes.
- Transparency: DeFi operates on public blockchains, which provide transparent and auditable transactions. All activities are recorded on the blockchain, allowing anyone to verify and audit the transactions, contracts, and protocols. This transparency reduces the risk of fraud and manipulation.
- Security: DeFi leverages blockchain technology, which is inherently secure due to its decentralized and immutable nature. Smart contracts, the building blocks of DeFi applications, are designed to execute transactions automatically without the need for intermediaries. Once deployed on the blockchain, they cannot be altered, ensuring greater security and trust in the system.
- Interoperability: DeFi protocols are often designed to be interoperable, allowing different applications and platforms to interact and share data seamlessly. This interoperability fosters innovation and allows for the creation of complex financial products and services by combining various DeFi building blocks.
- Programmability: Smart contracts in DeFi are programmable and can execute predefined actions automatically based on predefined conditions. This programmability enables the creation of self-executing financial agreements, automated investment strategies, and decentralized governance mechanisms, removing the need for manual intervention.
- Lower Costs: DeFi eliminates many intermediaries and associated fees, reducing transaction costs for users. Traditional financial systems involve numerous intermediaries, each charging fees for their services. defi use cases minimizes or eliminates these intermediaries, resulting in cost savings for users.
- Global Accessibility: DeFi operates on the internet and is not limited by traditional banking hours or geographical boundaries. It allows users to access financial services 24/7, enabling global participation in the decentralized ecosystem.
- Innovation and Experimentation: DeFi promotes innovation and experimentation in the financial sector. Developers can build new applications, protocols, and financial products using existing DeFi infrastructure. This fosters a vibrant ecosystem where new ideas can be tested and implemented rapidly.
- Community Governance: Many DeFi projects embrace community governance models, allowing token holders to participate in decision-making processes. This democratic approach enables users to have a say in the direction and development of the protocols they use.
